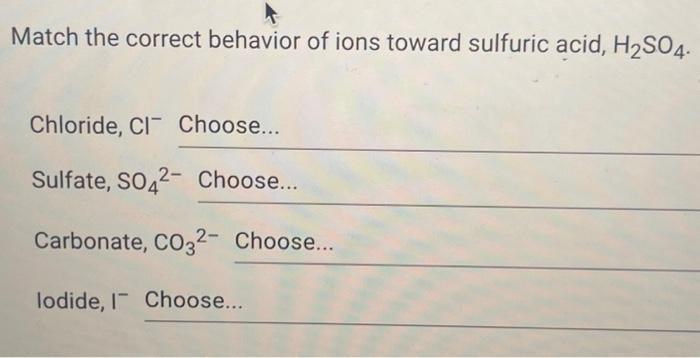
Match the correct behavior of ions toward sulfuric acid h2so4 – In the realm of chemistry, the behavior of ions toward sulfuric acid (H2SO4) holds great significance. Understanding this behavior is crucial for comprehending the intricate reactions and applications of this highly corrosive and powerful acid.
This comprehensive analysis delves into the chemical formula, corrosive nature, and strength of sulfuric acid. It meticulously examines the behavior of various ions in sulfuric acid, considering the influence of charge and concentration. Furthermore, it explores the reactions between ions and sulfuric acid, elucidating the products formed and the impact of acid concentration.
Sulfuric Acid and Its Properties
Sulfuric acid (H 2SO 4) is a highly corrosive, strong acid that plays a crucial role in various industrial processes. It is composed of hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen atoms, forming a molecular structure with two acidic protons (H +).
The corrosive nature of sulfuric acid arises from its ability to react with many organic and inorganic substances, including metals, releasing hydrogen gas. This property makes it a hazardous chemical that requires careful handling and storage.
As an acid, sulfuric acid is exceptionally strong. It completely dissociates in water, releasing its protons, which contributes to its high acidity and ability to donate protons to other molecules.
Behavior of Ions in Sulfuric Acid
The behavior of ions in sulfuric acid depends on their charge and the concentration of the acid. Ions with a higher charge tend to interact more strongly with the acidic protons of sulfuric acid.
| Ion Charge | Behavior in Sulfuric Acid |
|---|---|
| Positive (Cations) | Positively charged ions (cations) are attracted to the negatively charged sulfate ions (SO42-) in sulfuric acid, forming ion pairs or complex ions. |
| Negative (Anions) | Negatively charged ions (anions) compete with the sulfate ions for the acidic protons, leading to the formation of conjugate acids. |
The concentration of sulfuric acid also affects the behavior of ions. In dilute solutions, ions are more likely to form ion pairs or complex ions, while in concentrated solutions, they tend to remain free.
Reactions of Ions with Sulfuric Acid: Match The Correct Behavior Of Ions Toward Sulfuric Acid H2so4

Ions can react with sulfuric acid in various ways, depending on their charge and the concentration of the acid. Some common reactions include:
- Neutralization:Positively charged ions (cations) react with sulfuric acid to form salts and water. For example, sodium ions (Na +) react with sulfuric acid to form sodium sulfate (Na 2SO 4) and water (H 2O).
- Protonation:Negatively charged ions (anions) can react with sulfuric acid to form conjugate acids. For example, hydroxide ions (OH –) react with sulfuric acid to form hydronium ions (H 3O +) and sulfate ions (SO 42-).
- Precipitation:In some cases, ions can react with sulfuric acid to form insoluble precipitates. For example, barium ions (Ba 2+) react with sulfuric acid to form barium sulfate (BaSO 4), which precipitates out of solution.
The concentration of sulfuric acid affects the extent of these reactions. In dilute solutions, reactions tend to proceed more slowly and incompletely, while in concentrated solutions, reactions tend to be faster and more complete.
Applications of Sulfuric Acid

Sulfuric acid is a versatile chemical with numerous industrial applications, including:
- Fertilizer production:Sulfuric acid is used to produce phosphate fertilizers, such as ammonium phosphate and superphosphate, which are essential for crop growth.
- Battery manufacturing:Sulfuric acid is used as an electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, which are commonly found in cars and other vehicles.
- Petroleum refining:Sulfuric acid is used to refine crude oil and remove impurities, such as sulfur compounds and nitrogen compounds.
- Metal processing:Sulfuric acid is used to dissolve metals, such as copper and zinc, and to produce metal sulfates.
- Chemical synthesis:Sulfuric acid is used to synthesize a wide range of chemicals, including dyes, detergents, and pharmaceuticals.
The behavior of ions in sulfuric acid contributes to its industrial applications. For example, the ability of sulfuric acid to protonate and form conjugate acids is crucial for its use in fertilizer production, where it converts ammonia (NH 3) into ammonium ions (NH 4+), which are essential for plant growth.
Questions Often Asked
What is the chemical formula of sulfuric acid?
H2SO4
Why is sulfuric acid corrosive?
Due to its ability to donate protons and react with various substances, including water, metals, and organic compounds.
How does the concentration of sulfuric acid affect the behavior of ions?
Higher concentrations of sulfuric acid can lead to increased reactivity and the formation of different products in reactions.