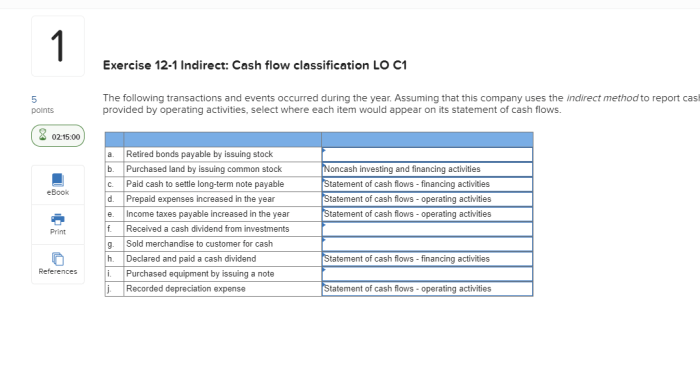
Indicate whether or not each item generates network externalities – As we delve into the topic of network externalities, we embark on a journey to understand their significance and impact on the products and services we use daily. Network externalities arise when the value of a good or service increases with the number of users, creating a mutually beneficial cycle.
This concept has far-reaching implications for businesses and consumers alike, shaping market dynamics and influencing technological advancements.
Network externalities can be direct or indirect, and their presence can have profound effects on industries. By exploring real-world examples and examining the factors that influence their strength, we gain a deeper appreciation for the role they play in our increasingly interconnected world.
Network Externalities: Definitions and Concepts
Network externalities arise when the value of a good or service increases as more people use it. This phenomenon occurs because the utility derived from a product or service is not only determined by its intrinsic characteristics but also by the size and activity of the network associated with it.
There are two main types of network externalities: direct and indirect.
Direct network externalities arise from increased usage. For example, the value of a telephone network increases as more people have telephones, as it allows users to connect with a larger pool of potential callers. Indirect network externalities arise from the presence of complementary products or services.
For example, the value of a video game console increases as more games are developed for it, as it provides users with a wider range of entertainment options.
Network externalities can have a significant impact on market dynamics. They can lead to the creation of dominant platforms, as users are more likely to adopt products or services that are already widely used. They can also create barriers to entry for new competitors, as it can be difficult to overcome the network effects enjoyed by established players.
Direct Network Externalities
Direct network externalities arise from increased usage. This occurs when the value of a good or service increases as more people use it. A classic example of a direct network externality is the telephone network. The more people who have telephones, the more valuable the network becomes for each individual user.
This is because each additional user increases the number of potential connections that can be made.
Other examples of products or services that exhibit direct network externalities include:
- Social media platforms
- Messaging apps
- Online marketplaces
- Video games
Compatibility and interoperability play an important role in direct network externalities. For example, the value of a video game console increases as more games are developed for it, as it provides users with a wider range of entertainment options. However, if the console is not compatible with other consoles or games, then the network externalities will be limited.
Indirect Network Externalities: Indicate Whether Or Not Each Item Generates Network Externalities
Indirect network externalities arise from the presence of complementary products or services. This occurs when the value of a good or service increases due to the availability of other products or services that complement it. A classic example of an indirect network externality is the ecosystem of apps that are available for smartphones.
The more apps that are available, the more valuable the smartphone becomes for each individual user.
Other examples of products or services that exhibit indirect network externalities include:
- Personal computers
- Operating systems
- Web browsers
- Cloud computing services
Platform effects and ecosystems play an important role in indirect network externalities. For example, the value of a personal computer increases as more software is developed for it, as it provides users with a wider range of functionality. However, if the personal computer is not compatible with other software or peripherals, then the network externalities will be limited.
Expert Answers
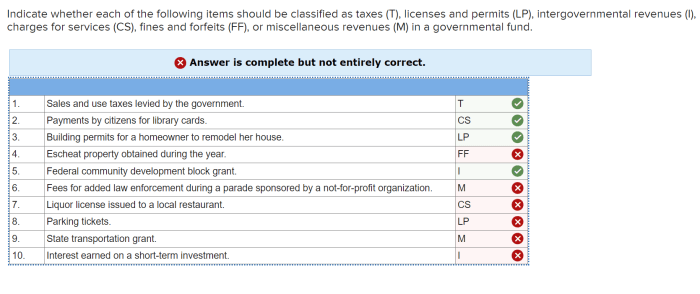
What are network externalities?
Network externalities occur when the value of a good or service increases as more people use it. This is because the increased usage leads to greater benefits for all users.
What are the two main types of network externalities?
Direct network externalities arise from increased usage, while indirect network externalities arise from the presence of complementary products or services.
How do network externalities influence market dynamics?
Network externalities can lead to market dominance and the emergence of platform ecosystems. They can also create barriers to entry for new competitors.