Consider a single crystal oriented such that the slip direction aligns precisely, leading to profound implications for material properties and engineering applications. This article delves into the significance of crystal orientation and slip direction, exploring their impact on material behavior and the techniques used to characterize and model these crucial aspects.
Understanding crystal orientation and slip direction is paramount in materials engineering, enabling the optimization of material performance for specific applications. By manipulating these factors, engineers can tailor materials to exhibit desired properties, such as enhanced strength, ductility, and toughness.
1. Introduction
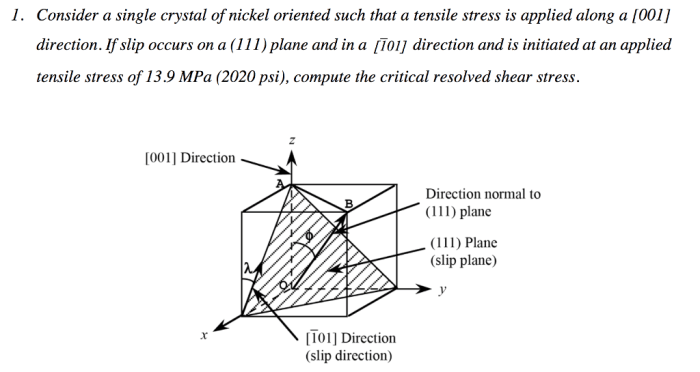
Single crystal orientation refers to the specific alignment of the crystal lattice in a single crystal material. The slip direction, on the other hand, represents the direction along which the crystal can deform plastically.
Considering both the crystal orientation and slip direction is crucial because they significantly influence the material’s properties and behavior.
2. Impact on Material Properties
The orientation of a single crystal and its slip direction can have a profound impact on its material properties, such as:
- Strength:The strength of a material is determined by its resistance to deformation. The orientation of the crystal lattice and the slip direction can influence the ease with which dislocations can move, thereby affecting the material’s strength.
- Ductility:Ductility measures a material’s ability to deform plastically without fracturing. The crystal orientation and slip direction can affect the number of slip systems available, which in turn influences the material’s ductility.
- Toughness:Toughness is a measure of a material’s resistance to fracture. The crystal orientation and slip direction can affect the formation and propagation of cracks, thereby influencing the material’s toughness.
3. Applications in Materials Engineering
Understanding crystal orientation and slip direction is essential in materials engineering for several reasons:
- Optimizing Material Performance:By controlling the crystal orientation and slip direction, engineers can tailor the material’s properties to meet specific application requirements.
- Case Study:In the aerospace industry, single crystals with specific orientations are used in turbine blades to enhance their strength and durability at high temperatures.
4. Characterization Techniques: Consider A Single Crystal Oriented Such That The Slip Direction

Various techniques are employed to characterize the crystal orientation and slip direction in single crystals:
- Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD):EBSD uses a focused electron beam to generate diffraction patterns that provide information about the crystal orientation at each point on the sample.
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD):XRD uses X-rays to determine the crystal structure and orientation of a sample by analyzing the diffraction patterns generated.
- Laue Diffraction:Laue diffraction uses a polychromatic X-ray beam to obtain diffraction patterns from single crystals, providing information about their orientation and crystal structure.
5. Modeling and Simulation

Modeling and simulation play a vital role in predicting the behavior of single crystals based on their orientation and slip direction:
- Crystal Plasticity Models:These models simulate the plastic deformation of single crystals by considering the interactions between dislocations and the crystal lattice.
- Finite Element Modeling (FEM):FEM can be used to simulate the mechanical behavior of single crystals under various loading conditions, taking into account their crystal orientation and slip direction.
- Case Study:In the automotive industry, modeling and simulation are used to optimize the design of engine components by predicting their behavior under different operating conditions.
FAQs
What is crystal orientation?
Crystal orientation refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms or molecules within a crystal lattice, defining the crystal’s shape and properties.
How does slip direction influence material properties?
Slip direction determines the direction of plastic deformation in a crystal, affecting the material’s strength, ductility, and toughness.
What techniques are used to characterize crystal orientation and slip direction?
Various techniques, such as X-ray diffraction, electron backscatter diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy, are employed to characterize crystal orientation and slip direction.