Embark on a geometric adventure with our Geometry Chapter 7 Practice Test! Get ready to sharpen your skills and delve into the fascinating world of angles, triangles, and circles. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to conquer any geometry challenge.
Our practice test mirrors the actual exam format, providing you with a realistic assessment of your understanding. Dive into a variety of question types, from multiple choice to short answer, to test your mastery of geometric concepts.
Understanding Geometry Chapter 7 Concepts
Geometry Chapter 7 delves into the fascinating world of polygons and their properties. Polygons are closed figures formed by three or more straight sides. Understanding the characteristics and relationships between different types of polygons is crucial in this chapter.
Types of Polygons
Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess. Some common types include:
- Triangle: A polygon with three sides.
- Quadrilateral: A polygon with four sides.
- Pentagon: A polygon with five sides.
- Hexagon: A polygon with six sides.
- Octagon: A polygon with eight sides.
Properties of Polygons
Each type of polygon has unique properties that distinguish it from others. These properties include:
- Interior angles: The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with ‘n’ sides is (n-2) – 180 degrees.
- Exterior angles: The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360 degrees.
- Diagonals: A diagonal is a line segment connecting two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon. The number of diagonals in a polygon with ‘n’ sides is (n – (n-3)) / 2.
Relationships between Polygons
Polygons can be related to each other in various ways:
- Regular polygons: Polygons with all sides and angles equal are called regular polygons.
- Similar polygons: Polygons with the same shape but different sizes are called similar polygons.
- Congruent polygons: Polygons with the same size and shape are called congruent polygons.
Understanding these concepts is essential for solving problems involving polygons, such as finding their area, perimeter, and angles. By grasping these fundamentals, students can develop a strong foundation in geometry and prepare for more advanced topics in the future.
Practice Test Structure and Format: Geometry Chapter 7 Practice Test
The Geometry Chapter 7 practice test is designed to assess your understanding of the concepts covered in the chapter. The test consists of a variety of question types, including multiple choice, true/false, and short answer questions.
The test has a time limit of 60 minutes and is worth a total of 100 points. The scoring system is as follows:
- Multiple choice questions: 5 points each
- True/false questions: 2 points each
- Short answer questions: 10 points each
Review of Geometry Chapter 7 Topics
Geometry Chapter 7 delves into a comprehensive exploration of angle relationships, triangle properties, and circle theorems. To solidify your understanding, let’s delve into a concise review of these essential topics.
Angle Relationships, Geometry chapter 7 practice test
Angle relationships are crucial in geometry, enabling us to analyze and solve various problems. Here are some key concepts:
- Supplementary Angles:Two angles that sum up to 180 degrees.
- Complementary Angles:Two angles that sum up to 90 degrees.
- Vertical Angles:Angles that are formed by two intersecting lines and are opposite to each other.
Triangle Properties
Triangles, the fundamental building blocks of geometry, exhibit distinct properties that govern their behavior:
- Triangle Sum Theorem:The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Exterior Angle Theorem:The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles.
- Triangle Inequality Theorem:The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side.
Circle Theorems
Circles, with their unique properties, play a significant role in geometry:
- Central Angle Theorem:The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of its intercepted arc.
- Inscribed Angle Theorem:The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc.
- Tangent-Secant Theorem:The square of the length of a tangent from a point outside a circle to the circle is equal to the product of the lengths of the secants drawn from the point to the circle.
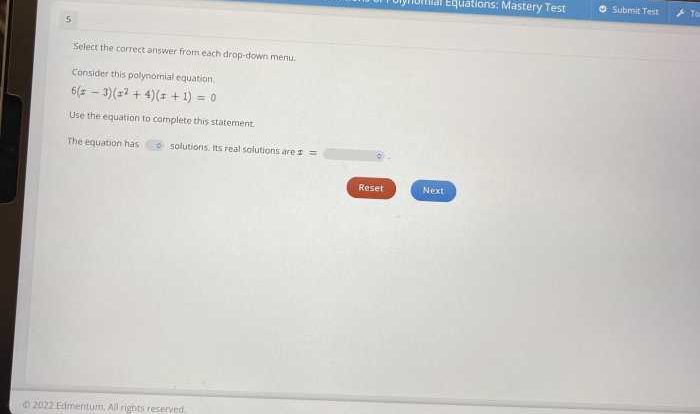
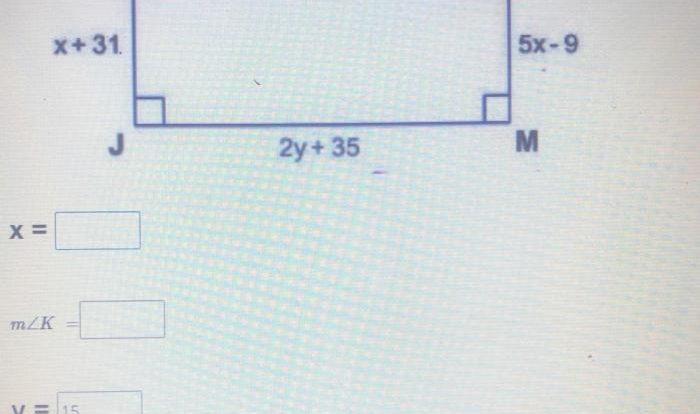
Practice Problems and Solutions
Practice problems and their solutions are essential for solidifying the concepts learned in Geometry Chapter 7. These problems provide students with the opportunity to apply geometric principles to real-world scenarios, reinforcing their understanding and developing their problem-solving skills.
The practice problems in this section cover the entire range of topics discussed in Geometry Chapter 7. Step-by-step solutions are provided for each problem, demonstrating the application of geometric principles and the logical thought process involved in solving geometric problems.
Sample Practice Problems
- Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 8 cm.
- Find the volume of a rectangular prism with a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 2 cm.
- Find the surface area of a sphere with a radius of 4 cm.
- Find the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm.
- Find the area of a trapezoid with bases of 6 cm and 8 cm and a height of 4 cm.
Additional Practice Problems
- Find the volume of a cone with a radius of 3 cm and a height of 5 cm.
- Find the surface area of a cylinder with a radius of 2 cm and a height of 6 cm.
- Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
- Find the area of a parallelogram with a base of 10 cm and a height of 6 cm.
- Find the volume of a pyramid with a square base of side length 4 cm and a height of 6 cm.
Test-Taking Strategies
Conquering Geometry Chapter 7 practice test requires strategic planning and execution. Effective test-taking strategies empower you to maximize your performance and showcase your understanding of the concepts.
Time management is crucial. Allocate time wisely for each question, prioritizing those you’re confident in. Don’t dwell on challenging questions initially; revisit them later with the time you save.
Question Selection
- Start with easier questions to build confidence and momentum.
- Identify questions that directly align with your strengths and areas of comfort.
- Eliminate obvious wrong answers to narrow down your choices.
Handling Challenging Questions
- Break down complex questions into smaller, manageable parts.
- Draw diagrams or sketches to visualize the problem.
- Consider alternative approaches or different perspectives.
Detailed FAQs
What topics are covered in the Geometry Chapter 7 Practice Test?
The practice test covers a wide range of geometry concepts, including angle relationships, triangle properties, and circle theorems.
What types of questions can I expect on the practice test?
The practice test includes a variety of question types, such as multiple choice, short answer, and true/false questions.
How much time will I have to complete the practice test?
The practice test is timed, and you will have a specific amount of time to complete it.