Bang cuu chuong in english – Embarking on a journey through the multiplication table in English, we delve into the fascinating world of numbers and their intricate relationships. From its historical roots to its practical applications, the multiplication table serves as a cornerstone of mathematical understanding.
Throughout history, the multiplication table has evolved as a tool for calculation, problem-solving, and decision-making. Its significance extends beyond the classroom, finding applications in fields as diverse as finance, engineering, and science.
History of the Multiplication Table
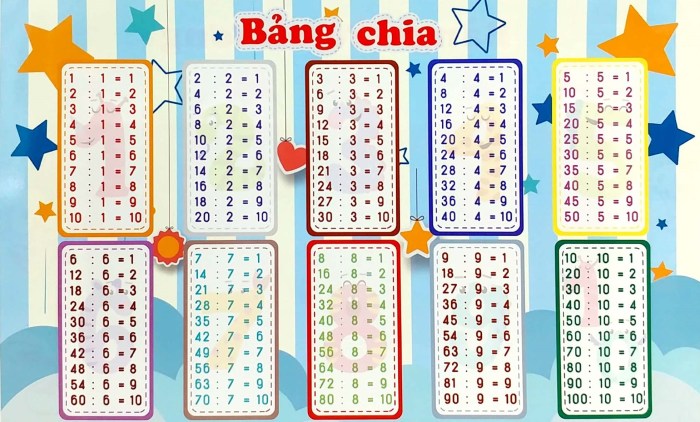
The multiplication table is a mathematical tool that has been used for centuries to simplify calculations. It is a tabular arrangement of the products of all pairs of numbers from 1 to 12. The multiplication table is an essential tool for students of all ages, and it is also used in many different fields, such as engineering, science, and business.
The history of the multiplication table can be traced back to ancient times. The earliest known multiplication table was found on a Babylonian clay tablet from around 2000 BC. This tablet contained a table of the products of all pairs of numbers from 1 to 50. The Babylonians used this table to perform calculations in their daily lives, such as calculating the area of a field or the volume of a cylinder.
The multiplication table was also known to the ancient Greeks and Romans. The Greek mathematician Euclid wrote about the multiplication table in his book Elements, which was written around 300 BC. The Roman mathematician Boethius wrote about the multiplication table in his book De Institutione Arithmetica, which was written around 500 AD.
The multiplication table was introduced to Europe in the Middle Ages by Arab mathematicians. The Arab mathematician al-Khwarizmi wrote about the multiplication table in his book The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing, which was written around 825 AD. This book was translated into Latin in the 12th century, and it became a popular textbook for students of mathematics in Europe.
The multiplication table is still used today as a valuable tool for performing calculations. It is an essential tool for students of all ages, and it is also used in many different fields, such as engineering, science, and business.
Different Methods Used to Create and Memorize the Multiplication Table in the Past
There have been many different methods used to create and memorize the multiplication table throughout history. Some of the most common methods include:
- Using a counting board: A counting board is a simple device that can be used to perform multiplication and division. To use a counting board, you place a number of counters on the board, and then you move the counters around to perform the multiplication or division operation.
- Using a multiplication wheel: A multiplication wheel is a mechanical device that can be used to perform multiplication. To use a multiplication wheel, you set the wheel to the two numbers that you want to multiply, and then you turn the wheel to find the product.
- Using a multiplication table: A multiplication table is a tabular arrangement of the products of all pairs of numbers from 1 to 12. To use a multiplication table, you simply look up the product of the two numbers that you want to multiply.
- Memorizing the multiplication table: Many people memorize the multiplication table by rote. This can be a difficult task, but it can be helpful for performing calculations quickly and easily.
Pedagogical Approaches to Teaching the Multiplication Table
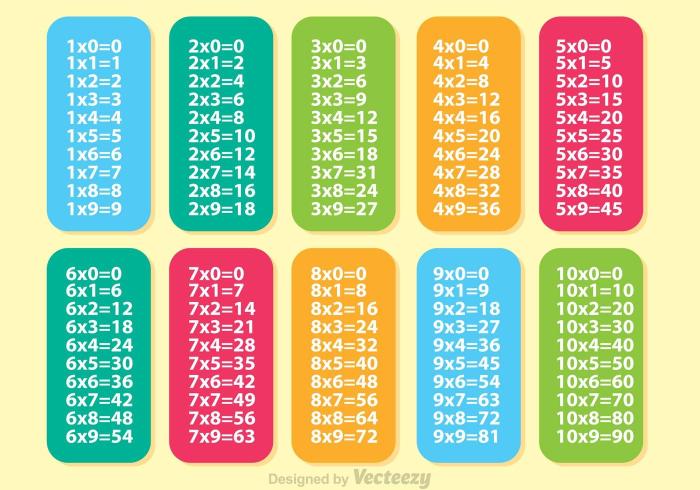
Teaching the multiplication table is a crucial step in developing students’ mathematical fluency and problem-solving abilities. Various pedagogical approaches can be employed to introduce and reinforce the multiplication facts, catering to diverse learning styles and ensuring effective comprehension.
Concrete Representation
- Using manipulatives such as blocks, counters, or arrays to demonstrate the multiplication concept in a tangible way, making it easier for students to visualize and understand the process.
- Creating physical models or drawings to represent multiplication problems, providing a hands-on approach that aids in conceptual understanding.
Visual Representation
- Introducing multiplication tables as colorful charts or posters displayed in the classroom, providing a constant visual reference for students.
- Using interactive digital tools or games that allow students to explore multiplication concepts through engaging visuals and animations.
Drill and Practice
- Providing regular practice opportunities through timed drills or worksheets, reinforcing the multiplication facts through repetition and recall.
- Incorporating games or activities that make practice fun and motivating, such as multiplication bingo or flashcards.
Mnemonic Devices
- Introducing mnemonic devices or rhymes to help students remember multiplication facts more easily, such as “five sixes are thirty” or “four nines are thirty-six.”
- Creating songs or chants that incorporate multiplication facts, making them more memorable and engaging for students.
Technology Integration
- Utilizing technology-based tools such as educational apps or online games to provide interactive and personalized learning experiences.
- Incorporating technology into practice activities, such as using digital flashcards or online quizzes, to enhance engagement and provide immediate feedback.
Applications of the Multiplication Table in Real-World Situations

The multiplication table, a fundamental concept in mathematics, extends beyond classrooms and textbooks, finding extensive applications in various fields and everyday life situations. Its significance lies in enabling individuals to solve practical problems, make informed decisions, and navigate through real-world scenarios.
The bang cuu chuong in English, also known as the multiplication table, is a handy tool for multiplying numbers quickly and accurately. It can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as calculating the area of a rectangle or finding the volume of a cube.
For instance, a hiker who weighs 985 N carrying a backpack that weighs 250 N would have a total weight of 1235 N. The bang cuu chuong in English can be a valuable resource for hikers and other outdoor enthusiasts who need to make quick calculations.
Finance
In finance, the multiplication table is crucial for calculations involving interest, compound interest, and investment returns. It helps individuals calculate the future value of investments, compare interest rates, and make informed financial decisions.
For instance, an individual investing $10,000 at a 5% annual interest rate can use the multiplication table to calculate the total value of their investment after 10 years. By multiplying the principal ($10,000) by the interest rate (0.05) and the number of years (10), they determine that the investment will grow to $16,288.95.
Engineering
In engineering, the multiplication table is essential for calculations involving forces, moments, and stresses. Engineers use it to design structures, calculate the strength of materials, and analyze the performance of mechanical systems.
For example, an engineer designing a bridge must calculate the force exerted on the bridge by a vehicle. By multiplying the weight of the vehicle (in pounds) by the acceleration due to gravity (32.2 ft/s^2), they determine the force that the bridge must withstand.
Science
In science, the multiplication table is used in various fields, including physics, chemistry, and biology. Scientists use it to calculate quantities such as energy, mass, and volume.
For instance, a physicist studying the motion of an object uses the multiplication table to calculate the object’s kinetic energy. By multiplying the object’s mass (in kilograms) by its velocity (in meters per second) squared, they determine the object’s kinetic energy in joules.
Cultural Variations in the Multiplication Table
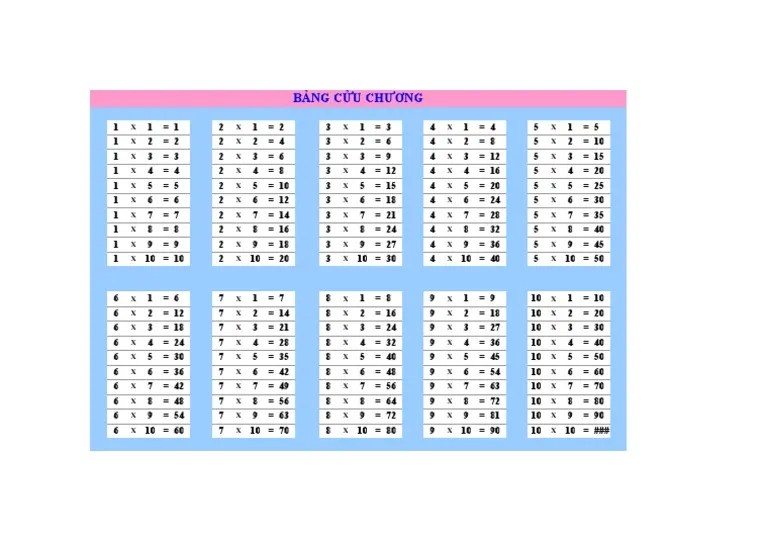
The multiplication table, a fundamental mathematical tool for understanding multiplication operations, exhibits cultural variations across different countries and languages. These variations manifest in the representation, usage, and pedagogical approaches to teaching the multiplication table.
In many Western cultures, the multiplication table is typically presented in a rectangular grid format, with the factors arranged along the top and side, and the products occupying the cells. However, in some Asian cultures, such as China and Japan, the multiplication table is often represented vertically, with the factors listed in a column and the products arranged horizontally.
Representation of the Multiplication Table
- Western cultures:Rectangular grid format, factors along the top and side, products in cells.
- Asian cultures (e.g., China, Japan):Vertical format, factors in a column, products horizontally.
- Arabic cultures:May use a variation of the Western grid format, but with different numerals and symbols.
Usage of the Multiplication Table
The usage of the multiplication table also varies across cultures. In some cultures, it is primarily used as a reference tool for memorizing multiplication facts. In other cultures, it is integrated into mathematical problem-solving and used as a tool for understanding numerical relationships.
- Memorization tool:Used to memorize multiplication facts and recall products quickly.
- Problem-solving tool:Used to solve multiplication problems and understand numerical relationships.
Pedagogical Approaches, Bang cuu chuong in english
The pedagogical approaches to teaching the multiplication table are influenced by cultural factors. In some cultures, rote memorization is emphasized, while in others, a more conceptual approach is favored.
- Rote memorization:Repeated practice and drills to memorize multiplication facts.
- Conceptual approach:Focus on understanding the concept of multiplication and developing strategies for solving multiplication problems.
These cultural variations in the multiplication table reflect the diverse ways in which mathematical knowledge is constructed and transmitted across different societies.
Advanced Applications of the Multiplication Table

The multiplication table, though seemingly basic, serves as a cornerstone for advanced mathematical concepts. It plays a pivotal role in algebra and calculus, enabling the exploration of complex mathematical relationships and solving intricate problems.
Multiplication in Algebra
In algebra, the multiplication table forms the foundation for polynomial multiplication. Polynomials, expressions consisting of variables and coefficients multiplied by each other, are multiplied using the distributive property and the multiplication table.
For example, (x + 2)(x- 3) = x(x – 3) + 2(x – 3) = x 2– 3x + 2x – 6 = x 2– x – 6.
The multiplication table also facilitates the simplification of algebraic expressions, such as factoring polynomials and solving equations.
Multiplication in Calculus
In calculus, the multiplication table underpins the concept of derivatives. The derivative of a function represents the instantaneous rate of change of the function. To find the derivative, the function is multiplied by a constant factor, which is determined using the multiplication table.
For instance, the derivative of f(x) = x2is f'(x) = 2x. This is because, according to the multiplication table, the derivative of x nis nx n-1.
Furthermore, the multiplication table is crucial for understanding integrals, the antiderivatives of functions. Integration involves multiplying the function by a constant factor, and the multiplication table provides the necessary values for this operation.
Frequently Asked Questions: Bang Cuu Chuong In English
What is the origin of the multiplication table?
The multiplication table has been used for centuries, with its origins tracing back to ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians and Egyptians.
How can I effectively teach the multiplication table to students?
Effective teaching methods include using visual aids, games, and repetitive practice. Technology can also be incorporated to enhance engagement and understanding.
Where is the multiplication table used in real-life situations?
The multiplication table finds applications in various fields, including finance (calculating interest), engineering (designing structures), and science (determining quantities).